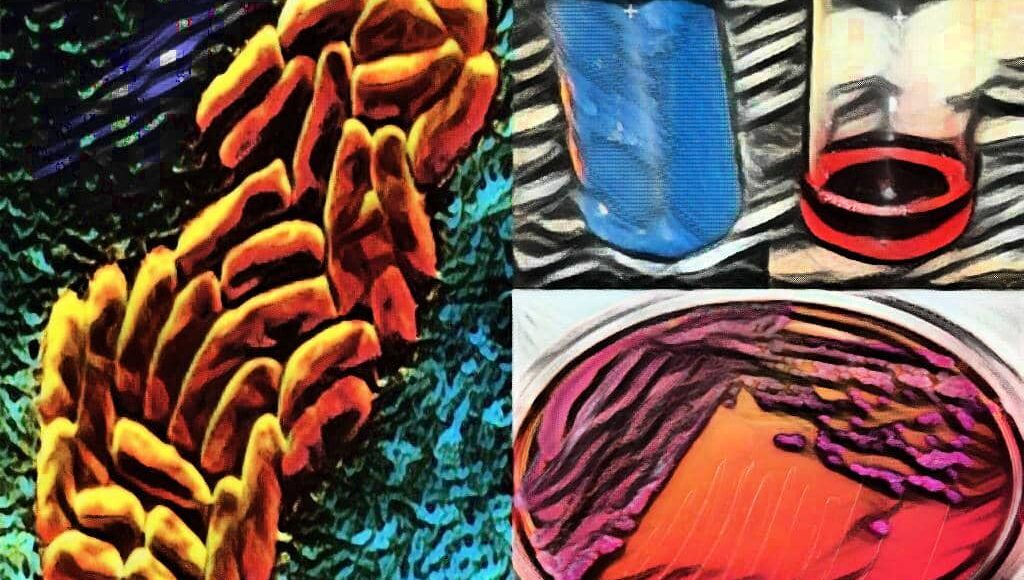
Check out the various Biochemical Tests For Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae)
Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… In this Article, we’re gonna discuss in detail about various biochemical tests for Klebsiella pneumoniae….. If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments…Thanks
There are so many biochemical reactions for the well known causative agent of Nosocomial Infections specially Pneumonia, UTI (Urinary Tract Infections), Septicemia, Pyogenic Infections and Sometimes Diarrhea i.e. the Klebsiella pneumoniae abbreviated as K. pneumoniae.
However, only a few reactions are most commonly used and are medically important for distinguishing pathogenic strains of K. pneumoniae from other non- pathogenic strains as well as from other species of Klebsiella, which are as follows:
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Indole Negative
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Citrate Positive
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Urease Positive
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Methyl red (MR) Negative
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Voges – Proskauer (VP) Positive
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Pink colored – LF colonies on MacConkey agar medium.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”checkmark” wrap=”b”]Purple colonies on EMB Agar medium without Green Metallic sheen.
Besides that of various biochemical reactions and Sugar fermentation tests, certain enzymatic reactions are also medically important to distinguish Klebsiella pneumoniae from other Klebsiella sp.

Below is the list of these Enzymatic Reactions and various other biochemical tests for Klebsiella pneumoniae which have great importance in research and for knowledge but are not routinely employed:
[table id=103/]
Klebsiella pneumoniae and other species of Klebsiella ferment various sugars producing acid with gas.
But these sugar fermentation tests are of no diagnostic value in routine laboratory tests except Glucose fermentation test which is commonly used to differentiate Klebsiella pneumoniae, which produces Acid with Gas, from other Pathogenic & non-pathogenic Klebsiella species especially from Klebsiellarhinoscleromatis, which do not produce gas during Glucose fermentation.
The other sugar fermentation tests which are described below are of great importance in research work.
[table id=104/]
That’s all about the various Biochemical tests for Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Two common biochemical tests used to identify bacteria are the catalase test, which detects the presence of the enzyme catalase, and the oxidase test, which detects the presence of the enzyme cytochrome oxidase.
Biochemical tests used to differentiate bacteria include tests for carbohydrate fermentation, motility, indole production, and urease production. Other tests, such as the Voges-Proskauer test and the citrate utilization test, can also be used.
The indole test can differentiate K. pneumoniae, which is indole-negative, from K. oxytoca, which is indole-positive.
The four commonly used biochemical tests for bacterial identification are the catalase test, oxidase test, indole test, and the urease test.
The four commonly used biochemical tests for bacterial identification are the catalase test, oxidase test, indole test, and the urease test. These tests help to identify different enzymes produced by the bacteria.
Biochemical tests used for bacterial identification include tests for the presence of enzymes such as catalase, oxidase, urease, and indole. Other tests may include tests for fermentation of specific carbohydrates, motility, and the ability to utilize citrate or produce hydrogen sulfide. These tests help to differentiate between different bacterial species based on their unique characteristics.