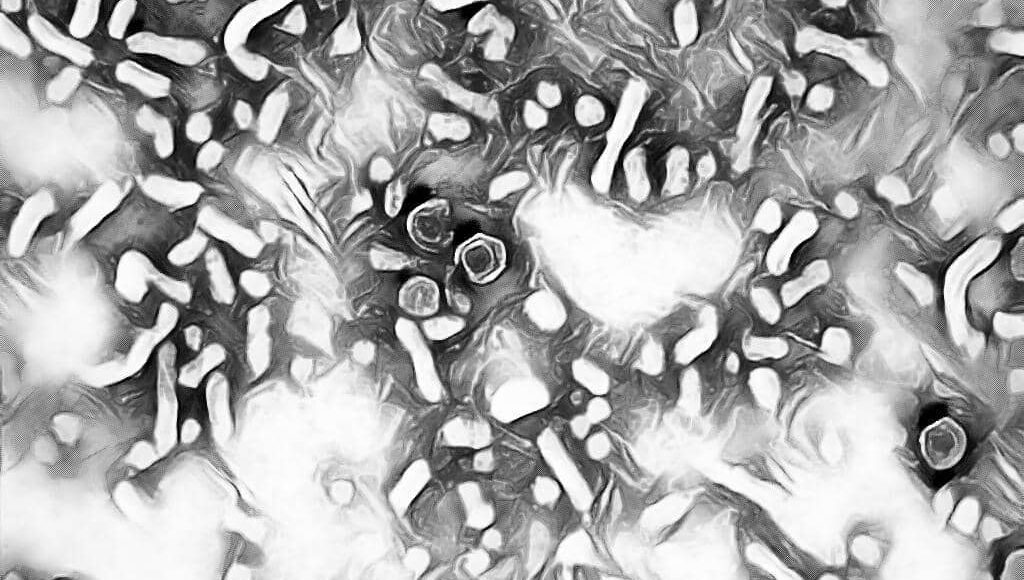
Let’s Discuss the Morphology, Transmission, Clinical Features & Laboratory Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… Before going into details, let’s discuss briefly the history of Hepatitis B Virus…..If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments….. Thanks
Brief Introduction to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The Hepatitis B Virus abbreviated as HBV was first observed in 1965 & named as Australia antigen.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Later on…. in 1968, it was found to be associated with serum hepatitis & the name has been changed to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV).
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV causes Type B hepatitis, the most widespread and the most important type of viral hepatitis.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV is the only hepatitis virus that contains DNA as genetic material.
What is the Morphology of Hepatitis B Virus ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV is a complex 42 nm double-shelled particle consist of an outer envelope & an inner core.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV is assigned to a separate family Hepadnaviridae.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The outer surface or envelope of virus contains hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg).
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The core of the virus consists of an icosahedral 27nm nucleocapsid, which contains Hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg).
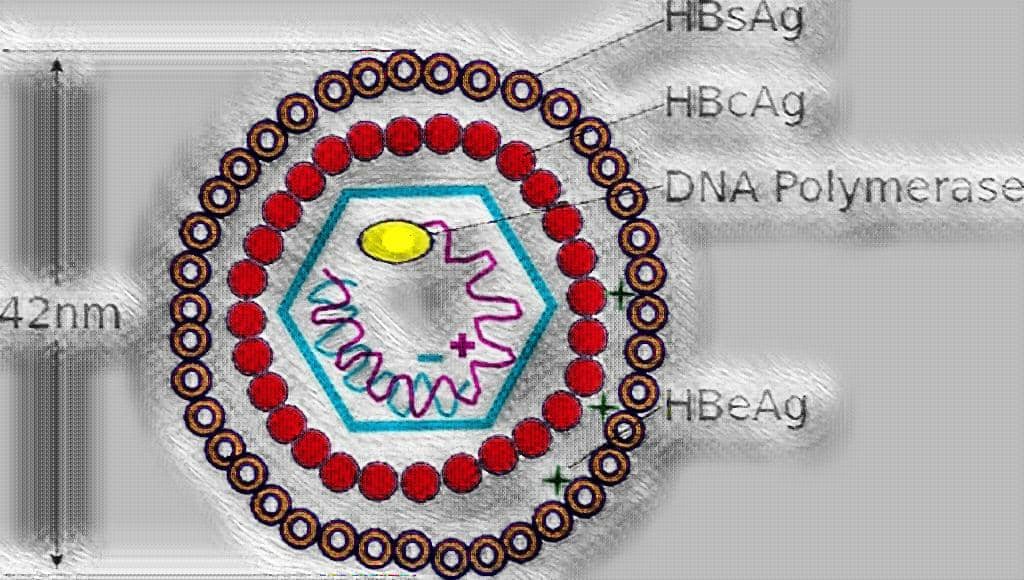
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Inside the core is the genome, a circular dsDNA & a DNA polymerase.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV, antigenically, have been divided into 3 types of particles as:-
- HBsAg – Hepatitis B Surface Antigen a.k.a. Australia antigen.
- HBcAg – Hepatitis B core Antigen a.k.a. Core antigen.
- HBeAg – Hepatitis B early Antigen a.k.a. Early antigen.
What are the Transmission Routes of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV is a blood-borne virus and the infection is transmitted by Parenteral, Sexual & Perinatal route.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Parenteral Route – Blood, Saliva, Breast Milk, Semen, Vaginal Secretions, Urine, Bile & Feces.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Sexual Route – the risk increases with no. of partners & sexual relationships, HBV infection has occurred after artificial insemination- semen donor screening is obligatory.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Perinatal Route – Congenital or vertical transmission is quite common from carrier mothers. Infection is usually acquired during birth by contact of maternal blood with the skin & mucosa of the fetus.
The Resistance Shown by Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBV is a relatively Heat Stable Virus than other hepatitis viruses.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Viable at room temperature for longer periods.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Heat at 60oC for 10 hours reduces infectivity by 100-1000 folds.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Exposure to hypochlorite or 2% glutaraldehyde inactivates infectivity but HBsAg may not be destroyed by such treatment.
Vaious Clinical features of Type B Hepatitis
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The incubation period is long, about 1 – 6 months.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The clinical features HBV are similar to that of the HAV.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] These include – Malaise, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly & Jaundice.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] In Severe cases – Liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma & chronic hepatitis are common.
Here is the Laboratory Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Lab diagnosis of HBV infection can be carried out by detection of Hepatitis B Antigens & antibodies which can be detected by sensitive tests like ELISA & RIA.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] HBcAg is not detectable in the serum but can be demonstrated in liver cells by immunofluorescence.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] The DNA levels of HBV can also be detected in serum by PCR.
What is the effective Prophylaxis of Hepatitis B Viral Infection (HBV Infection) ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] General preventive measures include avoiding the use of unsterile needles, syringes & other materials, avoid risky promiscuous sex, Health education, screening for HBsAg & HBeAg in blood donors.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Immunization includes- Both active & passive immunization is available. Intramuscular administration of the Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) as soon as possible after any accidental exposure to HBV infection, three doses of Hepatitis B vaccine at 0, 1 & 6 months are administered intramuscularly provides immunity against HBV for many years.
What are the possible Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] No specific antiviral treatment is available.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Interferon-alpha alone or in combination with other antiviral agents, e.g. famcyclovir, has been beneficial in some cases of chronic hepatitis.