Check Out the Various Biochemical Tests For Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes)
Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… In this Article, we’re gonna discuss in detail about various biochemical tests for Streptococcus pyogenes….. If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments…Thanks
There are so many biochemical reactions for the well known causative agent of Pyogenic infection i.e. the Streptococcus pyogenes but a few reactions are most commonly used and are medically important for distinguishing pathogenic strains of Streptococcus pyogenes from other non- pathogenic strains of S. pyogenes as well as from other species of Streptococcus which are as follows:
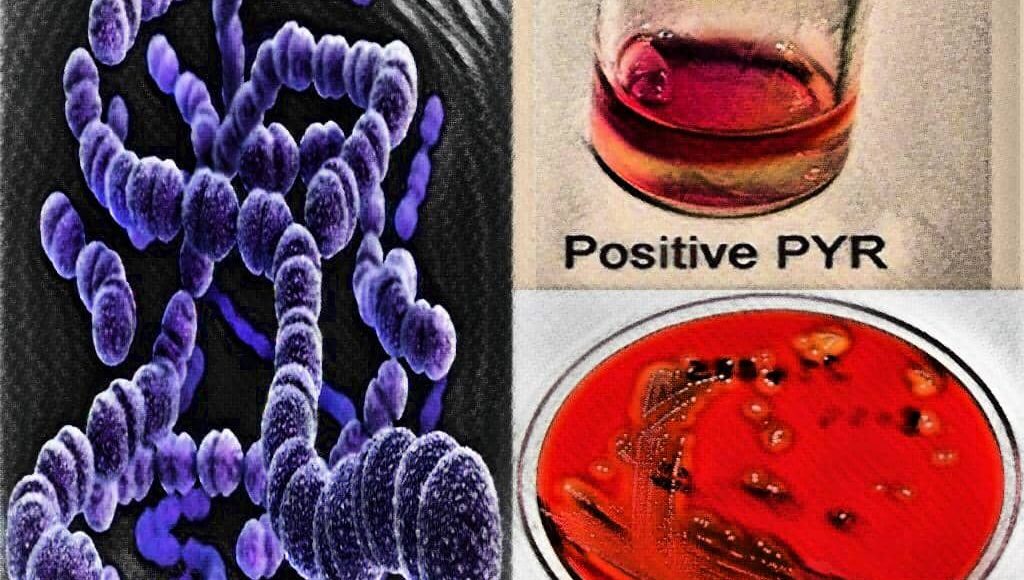
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Beta hemolysis on Blood agar
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Beta hemolysis and growth on PNF medium
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Beta hemolysis and Growth on Crystal Violet Blood Agar (CVBA)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Catalase Negative
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Insoluble in 10% Bile (differentiate S. pyogenes from S. pneumoniae)
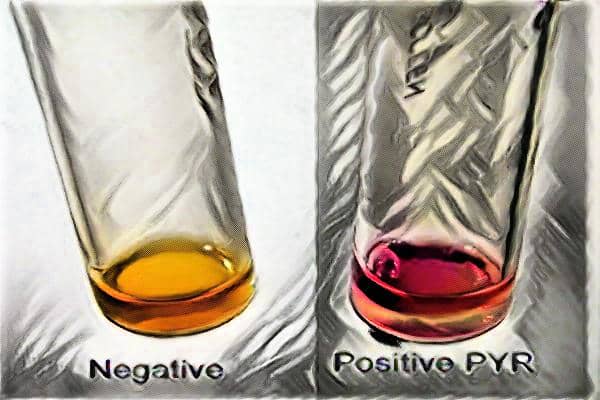
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] PYR hydrolysis

[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Unable to ferment Ribose (differentiate S. pyogenes from other Streptococci)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Pyrase production
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Sensitive to Bacitracin (differentiate S. pyogenes from other Hemolytic Streptococci)
Below is the list of various other biochemical tests for Streptococcus pyogenes which have great importance in research and for knowledge but are not routinely employed:
[table id=97 /]
Streptococcus pyogenes and other species of Streptococci ferment various sugars producing acid without gas.
But these sugar fermentation tests are of no diagnostic value in routine laboratory tests except Ribose fermentation test which is of great importance in differentiating Streptococcus pyogenes, which is Ribose Negative, from other Pathogenic & non-pathogenic Streptococci especially from Streptococcus equisimilis.
The other sugar fermentation tests which are described below are of great importance in research work.
[table id=98 /]
That’s all about the Biochemical tests for Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the commonly used biochemical tests for Staphylococcus include catalase test, coagulase test, and the slide coagulase test. For Streptococcus, the most common tests are the bacitracin susceptibility test, the optochin susceptibility test, the bile esculin test, and the PYR (L-pyrrolidonyl-β-naphthylamide) test.
The CAMP (Christie, Atkins, and Munch-Petersen) test can be used to distinguish between Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae. In this test, a culture of the test organism is streaked on a blood agar plate, and a strip of Staphylococcus aureus is streaked perpendicular to it. The test is positive if the growth of the test organism is enhanced in the shape of an arrowhead around the Staphylococcus aureus streak.
The optochin susceptibility test is used to identify Streptococcus pneumoniae and differentiate it from other alpha-hemolytic streptococci, including Streptococcus pyogenes. In this test, a zone of inhibition is observed around a paper disk containing optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) when the bacteria are susceptible to it. Streptococcus pyogenes is resistant to optochin, while Streptococcus pneumoniae is susceptible.
No, Streptococcus pyogenes does not grow on MacConkey agar, as this selective and differential agar is intended for the growth of gram-negative enteric bacteria.
Blood agar is the most common selective agar used for the growth of Streptococcus pyogenes. Other selective media used for the isolation of this organism include Todd-Hewitt agar, Columbia CNA agar, and Sheep blood agar.
One of the new diagnostic tests for Streptococcus is the Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay. This test is a nucleic acid amplification technique that uses a single temperature and a set of six primers to amplify target DNA sequences. It is rapid, sensitive, and specific for the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes and other beta-hemolytic streptococci.