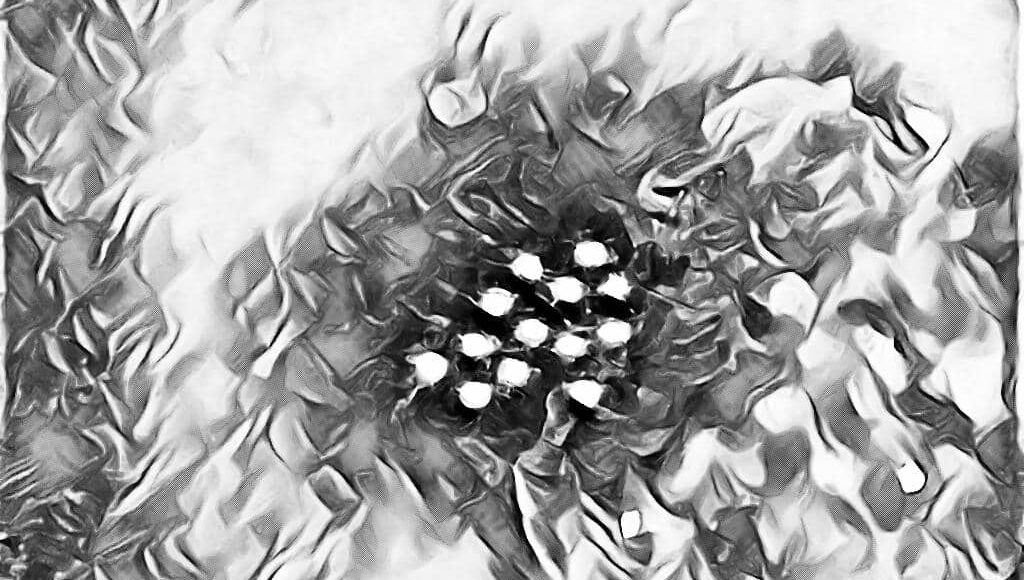
Morphology, Transmission, Clinical Features & Laboratory Diagnosis of Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… Before going into details, let’s First Discuss in brief about Hepatitis A Virus …..
A Brief Introduction to Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]The Hepatitis A virus (HAV) was first demonstrated by the Feinstone & co-workers in 1973 by using immunoelectron microscopy (IEM).
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV causes Type A hepatitis or Infectious Hepatitis, a subacute disease occurring mainly in children & young adults.
What is the Morphology of Hepatitis A Virus ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV is a 27 nm, non-enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus with an icosahedral symmetry.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV belongs to the Picornavirus family.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Only one serotype of this virus exists.
What are the Transmission Routes of Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]The Hepatitis A virus enters the body by the oral route through contaminated food, water or milk.
What type of Resistance is Shown By Hepatitis A Virus ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV is resistant to inactivation by heat at 60o C for 1 hour, ether & to pH 3, can survive at 4o C or below.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV is destroyed by autoclaving at 121oC, boiling for five minutes, formaldehyde (1:4000), by chlorine at 10-15 ppm for 30 minutes & inactivate by UV rays.
Various Clinical Features of Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]The large majority of infections are asymptomatic.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]The incubation period is 2-6 weeks.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Symptoms include Fever, Malaise, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Liver tenderness, usually subsides with Jaundice.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Rapidly fatal fulminant hepatitis is very rare.
The Laboratory Diagnosis of Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Specimen:- Feces or serum may be collected for the demonstration of the virus or its antibodies.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Direct demonstration:– The virus can be visualized by IEM in feces.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”] Serology:– IgM anti-HAV antibody appears during the late incubation period, reaches peak levels in 2-3 weeks & disappears after 3-4 months. IgG antibodies also appear & peaks in 3-4 months and persist much longer. ELISA kits are used to detect the presence of these antibodies in the feces & also can be detected by radioimmunoassay.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Biochemical tests:– Liver function tests such as serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and bilirubin level supplements the diagnosis.
What is the Prophylaxis of Hepatitis A Viral Infection (HAV Infection) ?
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]Improved sanitation & prevention of fecal contamination of food & water.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]HAV vaccination is available, the full course consists of two intramuscular injections of the vaccine. Protection lasts for 10-20 years.
[wp-svg-icons icon=”point-right” wrap=”i”]One attack of the disease gives life-long protection against HAV.