Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… In this Article, we’re gonna discuss the Formation of Various Blood Cells….. If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments…Thanks
What is the hematopoiesis ?
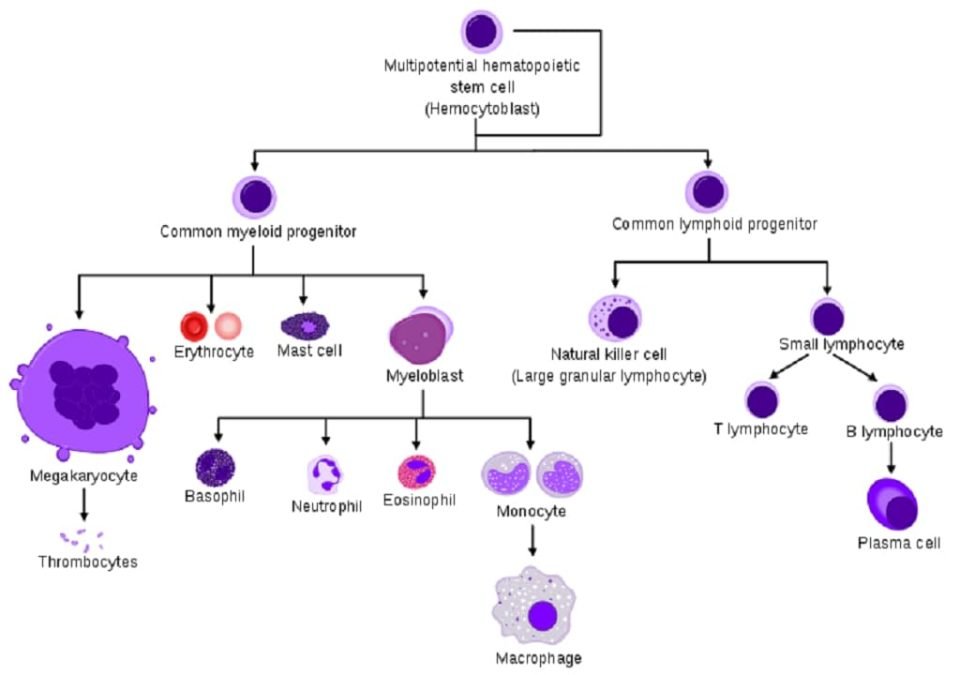
Hematopoiesis is the production, Development and the maturation of various cellular components of the blood
The cellular components of blood are developed from the Hematopoietic stem cells also known as Pluripotent Stem cells or totipotent stem cells which further differentiate and mature into typical blood cells.
The Pluripotent stem cells give rise to two types of Stem cells or lineages –
- Myeloid stem cells/Lineage – Differentiate in the Redbone marrow and form Erythrocytes, Granulocytes (Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils), Monocytes and Thrombocytes
- Lymphoid stem cells/Lineage – differentiates in the Redbone marrow and then migrates to the lymphoid tissue. They form T- and B- Lymphocytes.
The production of erythrocytes is called as Erythropoiesis; the leukocytes are called as Leucopoiesis and that of platelets is Thrombopoiesis.
Leucopoiesis is further subdivided into –
- Granulopoiesis – formation of granulocytes
- Monopoiesis – formation of monocytes
- Lymphopoiesis – formation of lymphocytes
What are the Sites of Hematopoiesis ?
- The site of Hematopoiesis depends on the age of the person as follows –
- In human embryo – Yolk sac is the main site of Hematopoiesis
- By the 3rd to 7th month of Intra-uterine life – Hematopoiesis occurs in liver and spleen.
- By the 7th month till birth – it starts in the bone marrow.
- From birth till maturity – occurs in bone marrow, spleen, and liver.
- In adults – Hematopoiesis occurs in the Central skeleton (Vertebrae, Sternum, Ribs, Skull, Sacrum, and pelvis), proximal ends of the long bones like Femur, Tibia, and Humerus.
What is Erythropoiesis?
It is the process of formation, development, and maturation of Red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Sites of production –
- The red bone marrow is the prime site for the production of RBC’s from birth till age 20
- After the age of 20 years, RBCs are mainly produced in the marrow of Vertebrae, Sternum, Ribs, and Pelvis
- After the gradual structural and functional maturation – the cells are released in peripheral circulation.
Regulation of Erythropoiesis – Erythropoietin is the hormone produced mainly by the kidneys, helps to regulate the process of Erythropoiesis so that the number of RBCs is sufficient to sustain adequate tissue oxygen levels.
STAGES OF ERYTHROPOIESIS NAME OF STAGE CELL SIZE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
1.) Proerythroblast 15-20 microns Deeply basophilic because of high RNA content. Large, Central and contains multiple Nucleoli and thick strand of chromatin are present.
2.) Early Normoblast 12-16 microns More basophilic. Gets smaller, coarse and granular chromatin are present, nucleoli may be absent.
3.) Intermediate Normoblast 10-14 microns Polychromatic – it contains mixture of basophilic RNA and Acidophilic Hemoglobin – Pinkish- blue. Nuclear chromatin – condensed, nucleoli absent.
4.) Late Normoblast 8-10 microns Acidophilic – pink color. Small and pushed to one side of the cell.
5.) Reticulocytes 7-9 microns Light pink, RNA strands are present. Degenerates.
6.) Erythrocytes 7.2-7.5 microns Pink – due to hemoglobin. Absent.
Reticulocytes are called as the juvenile RBCs or Immature RBCs.
Reticulocytes spend 1-2 days in the marrow than 1-2 days in circulation where it gets mature into Erythrocytes and attains biconcave shape.
Normal range of Reticulocytes –
- Adults – 0.5 – 2.5%
- Infants – 2 – 6%
What is Leukopoiesis?
It is the process of formation or production of leucocytes which normally occurs in the blood-forming tissue of the bone marrow. There are 3 independent series, which leads to the formation of 3 different types of white cells –
- Granulocytes – Granulopoiesis
- Lymphocytes – Lymphopoiesis
- Monocytes – Monopoiesis/ Monocytopoiesis
The formation of White Blood cells is regulated by –
- Stimulation by cytokines and Colony stimulating factor.
- Produced by Macrophages & T – lymphocytes.
- Activated by coming in contact with foreign organisms.
What is Granulopoiesis?
Granulopoiesis is the process of formation or production of Granulocytes that are the type of White blood cells that contains the granules in their cytoplasm, which begins at the Myeloblast and passes through the stages of a Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Metamyelocyte and Band cells and ultimately results in the formation of 3 types of Granulocytes – Neutrophils, Eosinophils & the Basophils.
S. No. STAGES OF GRANULOPOIESIS CELL SIZE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
1.) Myeloblast Large, 15-20 microns Thin rim of cytoplasm, Devoid of granules Large, Round or Oval nearly filling the cell.
2.) Pro - Myelocyte Slightly larger than Myeloblast, 15-25 microns. Contains primary or Azurophilic granules, are Peroxidase positive. Round, contains nucleoli - less prominent
3.) Myelocyte Small, 12 – 18 microns Specific or Secondary granules appears in cytoplasm Round or Oval, Nucleoli are absent.
4.) Meta – Myelocyte Small, 10 – 15 microns Both primary and secondary granules. Horse shoe or Kidney shapes, Nucleoli absent.
5.) Band cells Very small, 9 – 15 microns Pink with purple colored granules Band like nucleus, Condensed nuclear chromatin, further constricts to form lobes
6.) Segmented forms –
I) Neutrophil granulocytes
II) Eosinophil Granulocytes
III) Basophil Graulocytes
10-14 microns
10-14 microns
10-14 microns
Bluish pink with Fine, Light pink granules.
Pink colored with Coarse granules do not cover the nucleus.
Bluish color with coarse granules, covers the nucleus.
Deep purple with 2-5 lobes, condensed chromatin
Purple, Bilobed or Trilobed
Purple, Bilobed
What is Lymphopoiesis?
Lymphopoiesis is the process of formation or production of Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells that lack the granules in their cytoplasm, which begins at the Lymphoblast and passes through the stage of Prolymphocyte and ultimately results in the formation of mature Lymphocytes.
S. No. STAGES OF LYMPHOPOIESIS CELL SIZE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
1.) Lymphoblast Large, 10-20 microns Agranular & Scanty Large, Round or Oval with slightly condensed nuclear chromatin & few nucleoli.
2.) Prolymphocyte Slightly small, 10-18 microns Medium to deep homogeneous blue Centrally placed, Round or Indented which may have 0-1 nucleoli but is usually not seen.
3.) Lymphocyte i.) Large, 9-15 microns
ii.) Small, 7-8 micronsi.) Plentiful, colorless to light blue.
ii.) Narrow edge, Light or dark blue.i.) Oval / bulging, Central, Nucleoli absent.
ii.) Round/ Kidney shaped, compact chromatin.
What is Monopoiesis / Monocytopoiesis?
Monopoiesis or Monocytopoiesis is the process of formation of production of Monocytes, a type of White blood cells that lack the granules in their cytoplasm, which begins at the Monoblast, passes through the stage of Promonocyte and ultimately results in the formation of mature Monocytes.
S. No. STAGES OF MONOPOIESIS CELL SIZE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
1.) Monoblast Large, 12-20 microns Agranular, Light blue. Round / Oval, has fine chromatin, 1-4 nuclei, Central or eccentric.
2.) Promonocyte Large, 12-20 microns Scanty, Gray to pale blue & with rare or no granules. Sometimes Vacuoles may be present. Round, Indented nucleus with immature chromatin.
3.) Monocytes Large, 15-20 microns Dull, Gray-blue Round or Kidney shaped.
What is Thrombopoiesis?
Thrombopoiesis is the formation or production of Thrombocytes or Platelets in the bone marrow which is formed by fragmentation of mature Megakaryocyte membrane projections, begins at Megakaryoblast and passes through the stages of Promegakaryocyte and then the Megakaryocytes ultimately results in the formation of mature Thrombocytes or Platelets.
S. No. STAGES OF THROMBOPOIESIS CELL SIZE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS
1.) Megakaryoblast Large, 20-30 microns Scanty, Agranular cytoplasm Large, Oval or Kidney shaped with several nucleoli
2.) Promegakaryocyte Large, 25-30 microns Intensely basophilic, Agranular Large, Indented & may show mild lobulation
3.) Megakaryocyte Very Large, 50-100 microns Breaks up to form platelets (into tiny fragments) Multi lobed, Very large
4.) Platelets Small, 1-4 microns Basophilic, purple- reddish granules are present Anucleated cells
User Review
( votes)
Laboratory Hub aims to provide the Medical Laboratory Protocols & General Medical Information in the most easy to understand language so that the Laboratory Technologist can learn and perform various laboratory tests with ease. If you want any protocol to be published on Laboratory Hub, Please drop a mail at contact@laboratoryhub.com. Happy Learning!