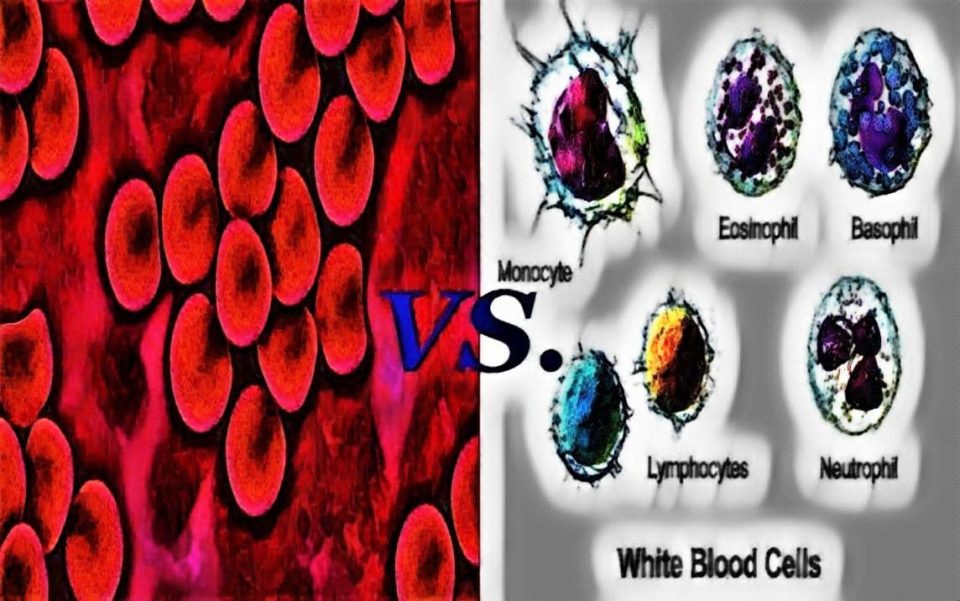
Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… In this Article, We’re gonna discuss the major difference between Red Blood Cells & White Blood Cells….. If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments….. Thanks
Beside the Platelets, the two most important cellular components present in our Blood are the Red Blood Cells and the White Blood Cells. Often people get easily confused between both the cells with respect to their Structure, Color, and functions.
Let’s discuss in brief about both the types of Blood Cells and later we’ll move to the major differences between them….
So, the Red blood cells also known as Erythrocytes and abbreviated as RBCs are the pigmented cells present in our blood consists of red color iron-containing pigment – Hemoglobin. The size of the RBCs is about 7.2 mm (microns) approximately and having a lifespan of about 120 days. The Red cells are mainly associated with the transportation of gases – Oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and Carbon dioxide from the tissues of the body to the lungs for excretion.
On the other hand, the White blood cells also known as Leucocytes or Leukocytes and abbreviated as WBCs are the non-pigmented cells hence called White cells. The size of the White blood cells varies as per the type of WBC, mainly 5 types of Leukocytes are present in our body and each one has different functions in our body. The lifespan of White blood cells also varies as per the type of White blood cell and the size ranges from 10-20 mm (microns) and that too varies according to the type of cell.
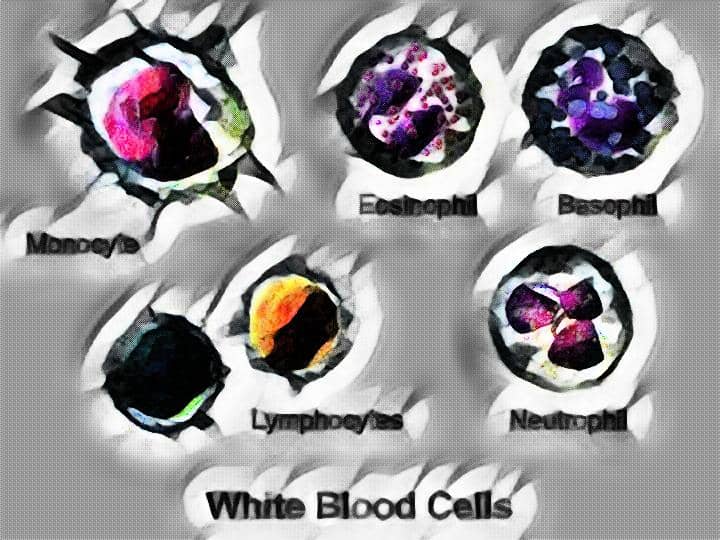
The White blood cells are mainly associated with the defense mechanism of our body and provide immunity against a variety of diseases as well as protects against any foreign particles, organisms, and Parasites. Moreover, Leukocytes are associated with the killing of cancer cells, productions of heparin, digestion of debris of dead cells etc….
Now let’s discuss the Major difference between Red blood cells and White Blood cells (RBCs VS. WBCs)…..
S. No. FEATURES RED BLOOD CELLS WHITE BLOOD CELLS
1.) Other Name Erythrocyte Leucocyte / Leukocyte
2.) Abbreviation RBCs WBCs
3.) Shape Red Blood Cells are Bi-Concave disc shaped cells White blood cells are Irregularly circular cells
4.) Size On an average the Red Blood Cells measure about 7.2 micrometers The size of White blood cells varies as per the type of WBC as follows:
Neutrophil - 10-14 µm
Eosinophil - 10-14 µm
Basophil - 10-12 µm
Lymphocyte - 15-20 µm
Monocyte - 12-18 µm
5.) Nuclei Red Blood Cells are Non - nucleated cells. White Blood Cells are nucleated cells.
6.) Process of Formation The process of formation of Red Blood Cells is known as Erythropoiesis. The Formation of various types of White Blood Cells is known as Leucopoiesis. Individually, the formation of Neutrophil, Eosinophil and Basophil is known as Granulopoiesis; formation of Monocytes is Monopoiesis and that of Lymphocytes is known as Lymphopoiesis.
7.) Color As the name suggests, the cells are Red in Color due to the presence of Hemoglobin. White blood cells are colorless as colored pigment is absent in WBCs.
8.) Pigment In Red Blood Cells, Iron-containing pigment is present i.e. Hemoglobin. No pigment is present in White blood cells.
9.) Types of cells Only one type of Red Blood Cells are present in humans. There are 5 types of White Blood Cells are Present in Human body divided into Granulocytes (Neutrophils, Eosinophils & Basophils) and Agranulocytes (Lymphocytes & Monocytes)
10.) Life span On an average the life span of Red Blood Cells is 120 days. The life span of various types of White Blood Cells is as follows:
Neutrophils - 2-4 days
Eosinophils - 10-14 days
Basophils - 10-15 days
Lymphocytes - 3 weeks-1 year
Monocytes - 3-5 days
11.) Productions The Red Blood cells are formed in Red Bone Marrow. The White Blood Cells are produced in White Bone Marrow, Lymph nodes & Spleen etc.
12.) Motility of Cells RBCs are Non-motile cells in the blood. WBCs are motile cells in the blood.
13.) Circulation The Red Blood Cells mainly circulate in Cardiovascular system. The White Blood Cells mainly circulate in Cardiovascular system and Lymphatic system.
14.) Movement The Red Blood Cells move in blood vessels eventually squeezing through capillaries giving O2 and nutrients to body cells and taking CO2 from the tissues. The White Blood Cells leave the blood vessels and move to the injury site. Capable of diapedesis-squeeze between cells of blood vessel walls.
15.) Type of Movement in Vessels The Red Blood cells just move into the Blood vessels and never leaves it unless there is any abnormality or injury. The White Blood Cells can leave circulation via capillaries and land in tissues.
16.) Normal Count In a healthy human body the Red Cells are present as follows:
In Males - 4.8-5.5 million/ mm3
In Females - 4-5 million/ mm3In a Healthy individual 4000 - 11000 WBCs are present per mm3
17.) Physiological Abnormalities Most commonly the Red cell count elevates at high altitudes or after strenuous physical exercise. Normally, in infants 20000 White cells are present per mm3 and also in case of Physical & Emotional stress the WBC count elevates.
18.) Pathological Abnormalities The most common Pathological condition associated with Red Blood Cells is Anemia. The most common pathological condition associated with White Blood cells is Infections and Leukemia.
19.) Rouleaux formation Rouleaux formation (stacks of cells) is commonly observed in Red Blood cells. Rouleaux formation does no takes place in White Blood Cells.
20.) Primary Function Transport of Gases and Nutrients Provide Immunity against infections - Defense system of out body.
21.) Granules in cell Absent Present in Some (Neutrophils, Eosinophils & Basophils)
That’s All about the Major Difference between Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells (RBCs VS. WBCs)
User Review
( votes)
Laboratory Hub aims to provide the Medical Laboratory Protocols & General Medical Information in the most easy to understand language so that the Laboratory Technologist can learn and perform various laboratory tests with ease. If you want any protocol to be published on Laboratory Hub, Please drop a mail at contact@laboratoryhub.com. Happy Learning!