Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… In this Article, We’re gonna discuss the Capsule Staining Technique….. If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments….. Thanks
What is the Capsule Staining technique?
A capsule in bacteria is the result of amorphous viscid secretion released by the bacteria. When this secretion remains loose and un-demarcated it is called a slime layer and when it is organized into a sharply defined structure it is called as Capsule.
Most of the capsules are made up of polysaccharides but there are many which are composed of Polypeptides (Proteins).
Capsules are usually fragile and can easily be destroyed or distorted by heating so the capsule staining is designed in such a way that maintains the overall morphology of bacteria as well as preserved the Capsule structure so that we can easily identify it.
Also, to get the better results and to enhance the size of the bacterial capsule a drop of serum can be used while preparing a smear which makes it more convenient to observe bacterial capsule with a typical compound/light microscopes.
There is no use of Complex processes and multiple strong reagents or stains in Capsule staining process and simplest methods like India ink method gives the satisfactory results so that we can easily determine the presence or absence of capsule in the bacterial cell.
Heat fixing is also avoided as it will destroy or distort the capsule which makes it more convenient and moreover the newbie’s to microbiology can easily do it and explore more in the microbial world….
Briefly, in Capsule staining technique, the background and the bacterial cell body is stained whereas capsule remains colorless. However, the result varies as per the methodology used for capsule staining.
Here is the Principle of Capsule Staining
Firstly, let’s discuss the bacterial cell structures which are involved in this staining technique and later on we’ll move to the principles involved in capsule staining technique.
A capsulated bacterium acquires a capsule around its body which appears as a clear halo. A Bacterial capsule is non-ionic in nature, so there is no or very minute possibility that the acidic or basic stains will adhere to their surfaces so it remains colorless.
The excellent way to demonstrate the capsule is to stain the bacterial cell body and the background leaving the bacterial capsule as colorless.
The Bacterial cell body is stained best with the Basic stains like Crystal violet, Safranine, Methylene blue etc. whereas the background is stained best with the Acidic stains which include the India ink, Nigrosin, Eosin, Congo red etc.
There are numerous methods available for the demonstration of the capsule in bacterial cells. The result of the staining varies as per the Method followed but commonly all the methods have one thing in common that it stains the bacterial cell, capsule and/or Background. The Two most commonly used methods are as follows:
The India ink method or Nigrosin method of Capsule Staining
This one is the easiest method of capsule staining. In this technique, two dyes are used that is Crystal violet and the India ink / Nigrosin.
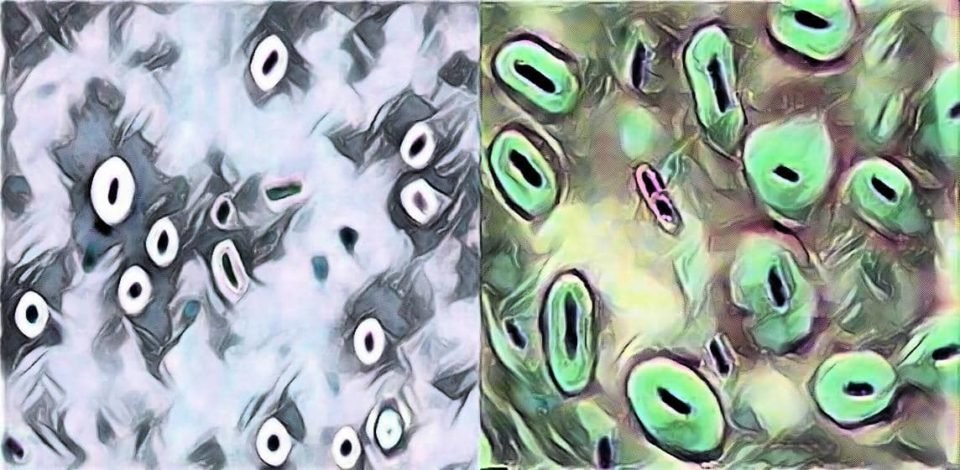
The Capsule of the bacterial cell appears as a clear halo around the stained bacterial cell body and the Dark background (color depends upon the dye used – India ink or Nigrosin).
The Anthony’s stain method of Capsule Staining
This one is another most commonly used method of Capsule staining. In this technique, the crystal violet stain is used as the primary stain.
Besides that, a 20% solution of copper sulfate is used which plays an important role in staining procedure by acting as a decolorizing agent as well as Counterstain.
20% CuSO4 decolorizes the bacterial capsules by removing the Crystal violet that sticks on it but has no such effect on bacterial cell body and it also stains the capsule which later appears as faint blue color zone or halo around purple bacterial cell body.
One important thing to note here is that there is no mordant and no strong decolorizers are used.
Here is the list of Materials Required for Capsule Staining Technique
- Microscopic glass slide.
- Inoculating loop.
- Spirit Lamp.
- Staining Rack.
- Wash bottle.
- Microscope (with 100X objective lens).
For India ink / Nigrosin method
- India Ink / Nigrosin (10% solution)
- Crystal violet (1% solution)
For Anthony’s Stain method
- Crystal violet (1% solution)
- Copper Sulfate (20% Solution)
The procedure of Capsule Staining Technique
The procedure of capsule staining using India ink / Nigrosin method
Take a clean, Dry, Scratch and Grease free Microscopic glass slide and place a drop of India ink or Nigrosin on it at one end near the edge.
Take a small portion of the bacterial colony or a loopful of broth culture with the help of sterilized Inoculating loop.
Mix well the culture with dye taken on the Glass slide.
Now, take another Microscopic Glass slide, place it near to the specimen-dye mixture at an angle of about 30° – 45°.
Move the slide toward the drop of the specimen-dye mixture until the contact is made with the drop at the specific angle. Then move the spreader slide smoothly and rapidly forward over the specimen slide, drawing the dye mixture behind it into a thin film.
Allow the smear to Air dry.
Note: Do not Heat as heat will melt the capsule and distorts the actual shape of the bacterial cell.
Now, Flood the smear slide with crystal violet solution for 1 minute and rinse carefully and gently with water.
Note: Be cautious while doing this step as water may remove the capsule from the cell as well as it may wash out the smear
Allow the smear slide to air dry.
Note: Do not Blot dry the slide as it may distort the capsule as well as the smear.
Observe under the microscope at High power objective (45X) and oil immersion (100X) objectives. To easily visualize the capsule make sure to decrease the amount of light while observing under the microscope.
The procedure of capsule staining using Anthony’s stain method
The procedure of Anthony’s stain method is quite similar to that of India ink / Nigrosin method initially which is as follows:
Take a clean, Dry, Scratch and Grease free Microscopic glass slide and place a drop of Crystal violet on it at one end near the edge.
Take a small portion of the bacterial colony or a loopful of broth culture with the help of sterilized Inoculating loop.
Mix well the culture with dye taken on the Glass slide.
Now, take another Microscopic Glass slide, place it near to the specimen-dye mixture at an angle of about 30° – 45°.
Move the slide toward the drop of the specimen-dye mixture until the contact is made with the drop at the specific angle. Then move the spreader slide smoothly and rapidly forward over the specimen slide, drawing the dye mixture behind it into a thin film.
Allow the smear to Air dry.
Note: Do not Heat as heat will melt the capsule and distorts the actual shape of the bacterial cell.
Now, Tilt the smear slide and rinse it with the 20% copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution.
Note: Do not Blot dry the slide as it may distort the capsule as well as the smear.
Observe under the microscope at High power objective (45X) and oil immersion (100X) objectives. To easily visualize the capsule make sure to decrease the amount of light while observing under the microscope.
Observations & Results of Capsule Staining Technique
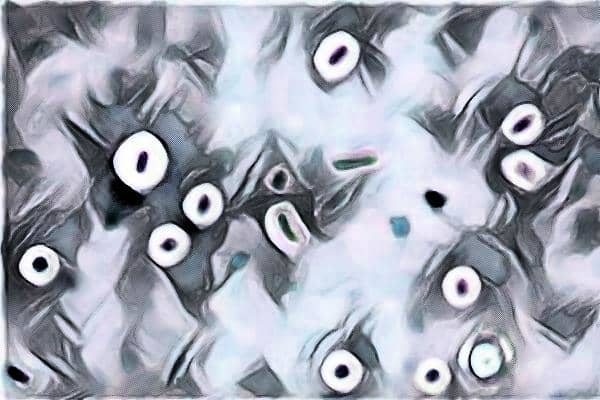
Results of Capsule staining using India ink / Nigrosin Method
The capsule appears as the Clear halo or clear zone around the purple colored bacterial cell body on a dark background. The Background color is due to the India ink or Nigrosin whatever you’ll use.

Results of Capsule staining using Anthony’s stain Method
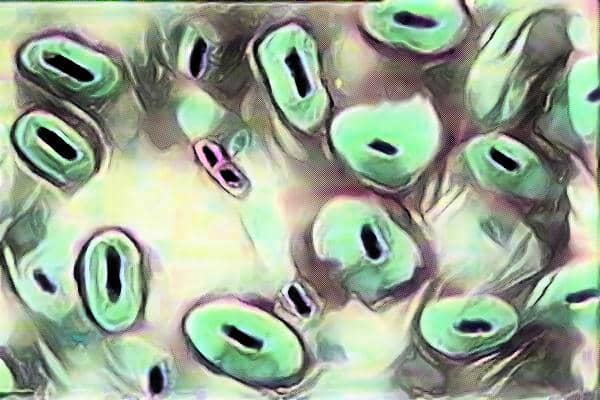
The capsule appears as the Faint blue halo around the purple bacterial cell body on a transparent background as there is no background stain is used in this technique.
Things to be Noted Here…..
By using India ink / Nigrosin technique, we stain the background and bacterial cell body, not the bacterial capsules actually.
By Anthony’s Stain method we stain the Bacterial cell body as well as the Capsule but not the Background.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the principle for capsule staining?
Capsule staining principle involves the use of acidic and basic stains to visualize the bacterial capsule, which is a protective layer surrounding some bacterial cells. The capsule resists simple staining and is usually invisible under a microscope. Therefore, capsule staining is done to highlight the capsule and distinguish it from the bacterial cell.
Q2. What are the steps in a capsule staining procedure?
The capsule staining procedure involves the following steps: (1) preparing a bacterial smear on a slide, (2) air-drying the smear, (3) heat-fixing the smear, (4) flooding the smear with an acidic stain, (5) washing off the excess stain with distilled water, (6) flooding the smear with a basic stain, (7) washing off the excess stain with distilled water, and (8) air-drying the slide before examining it under a microscope.
Q3. What are the methods of staining bacterial capsule?
The methods of staining bacterial capsule include the following: (1) capsule staining with acidic and basic stains, (2) India ink staining, (3) Maneval’s capsule stain, (4) Anthony’s capsule stain, and (5) Kinyoun’s capsule stain.
Q4. What is the principle and procedure of simple staining?
The simple staining principle involves the use of a single dye to color bacterial cells and make them visible under a microscope. The procedure involves the following steps: (1) preparing a bacterial smear on a slide, (2) air-drying the smear, (3) heat-fixing the smear, (4) flooding the smear with a basic or acidic dye, (5) washing off the excess stain with distilled water, and (6) air-drying the slide before examining it under a microscope.
Q5. What is the principle of staining experiment?
The principle of staining experiment involves the use of a staining agent to enhance the contrast and visibility of biological specimens under a microscope. The staining agent binds to specific cellular components and causes them to appear darker or lighter than the surrounding background.
Q6. What are methods of staining?
The methods of staining include the following: (1) simple staining, (2) differential staining (e.g., Gram staining), (3) special staining (e.g., capsule staining), and (4) negative staining.
User Review
( votes)
Laboratory Hub aims to provide the Medical Laboratory Protocols & General Medical Information in the most easy to understand language so that the Laboratory Technologist can learn and perform various laboratory tests with ease. If you want any protocol to be published on Laboratory Hub, Please drop a mail at contact@laboratoryhub.com. Happy Learning!