Hey, Good to see you here 😀 …… Before going into details, let’s discuss briefly the history of Hepatitis B Virus…..If you have any queries, don’t forget to mention in Comments….. Thanks
Brief Introduction to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
The Hepatitis B Virus abbreviated as HBV was first observed in 1965 & named as Australia antigen.
Later on…. in 1968, it was found to be associated with serum hepatitis & the name has been changed to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV).
HBV causes Type B hepatitis, the most widespread and the most important type of viral hepatitis.
HBV is the only hepatitis virus that contains DNA as genetic material.
What is the Morphology of Hepatitis B Virus ?
HBV is a complex 42 nm double-shelled particle consist of an outer envelope & an inner core.
HBV is assigned to a separate family Hepadnaviridae.
The outer surface or envelope of virus contains hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg).
The core of the virus consists of an icosahedral 27nm nucleocapsid, which contains Hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg).
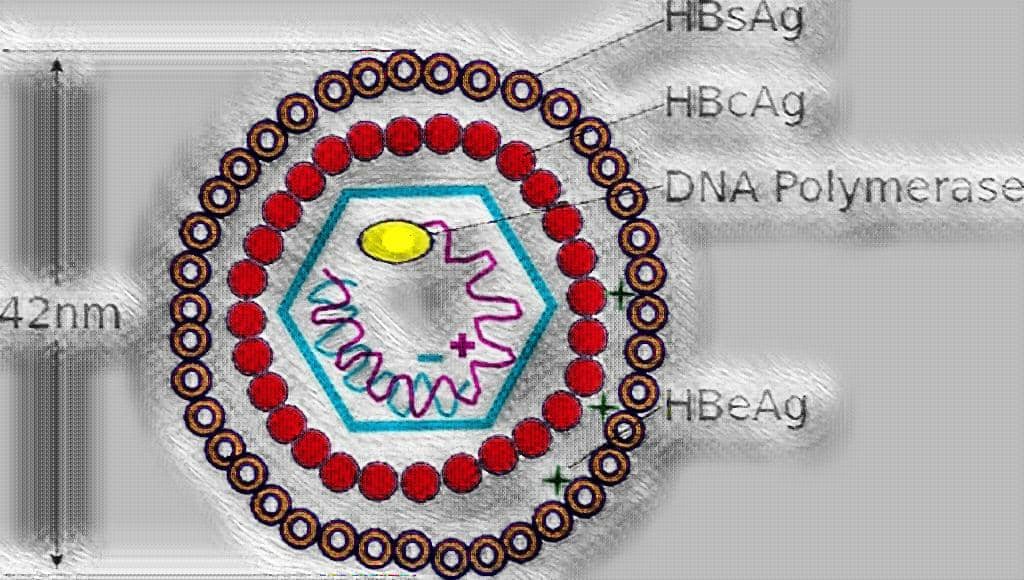
Inside the core is the genome, a circular dsDNA & a DNA polymerase.
HBV, antigenically, have been divided into 3 types of particles as:-
- HBsAg – Hepatitis B Surface Antigen a.k.a. Australia antigen.
- HBcAg – Hepatitis B core Antigen a.k.a. Core antigen.
- HBeAg – Hepatitis B early Antigen a.k.a. Early antigen.
What are the Transmission Routes of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ?
HBV is a blood-borne virus and the infection is transmitted by Parenteral, Sexual & Perinatal route.
Parenteral Route – Blood, Saliva, Breast Milk, Semen, Vaginal Secretions, Urine, Bile & Feces.
Sexual Route – the risk increases with no. of partners & sexual relationships, HBV infection has occurred after artificial insemination- semen donor screening is obligatory.
Perinatal Route – Congenital or vertical transmission is quite common from carrier mothers. Infection is usually acquired during birth by contact of maternal blood with the skin & mucosa of the fetus.
The Resistance Shown by Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
HBV is a relatively Heat Stable Virus than other hepatitis viruses.
Viable at room temperature for longer periods.
Heat at 60oC for 10 hours reduces infectivity by 100-1000 folds.
Exposure to hypochlorite or 2% glutaraldehyde inactivates infectivity but HBsAg may not be destroyed by such treatment.
Vaious Clinical features of Type B Hepatitis
The incubation period is long, about 1 – 6 months.
The clinical features HBV are similar to that of the HAV.
These include – Malaise, Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly & Jaundice.
In Severe cases – Liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma & chronic hepatitis are common.
Here is the Laboratory Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Lab diagnosis of HBV infection can be carried out by detection of Hepatitis B Antigens & antibodies which can be detected by sensitive tests like ELISA & RIA.
HBcAg is not detectable in the serum but can be demonstrated in liver cells by immunofluorescence.
The DNA levels of HBV can also be detected in serum by PCR.
What is the effective Prophylaxis of Hepatitis B Viral Infection (HBV Infection) ?
General preventive measures include avoiding the use of unsterile needles, syringes & other materials, avoid risky promiscuous sex, Health education, screening for HBsAg & HBeAg in blood donors.
Immunization includes- Both active & passive immunization is available. Intramuscular administration of the Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) as soon as possible after any accidental exposure to HBV infection, three doses of Hepatitis B vaccine at 0, 1 & 6 months are administered intramuscularly provides immunity against HBV for many years.
What are the possible Treatment of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ?
No specific antiviral treatment is available.
Interferon-alpha alone or in combination with other antiviral agents, e.g. famcyclovir, has been beneficial in some cases of chronic hepatitis.
User Review
( votes)
Laboratory Hub aims to provide the Medical Laboratory Protocols & General Medical Information in the most easy to understand language so that the Laboratory Technologist can learn and perform various laboratory tests with ease. If you want any protocol to be published on Laboratory Hub, Please drop a mail at contact@laboratoryhub.com. Happy Learning!